Ciprofloxacin salt and salt co-crystal with dihydroxybenzoic acids
Abstract
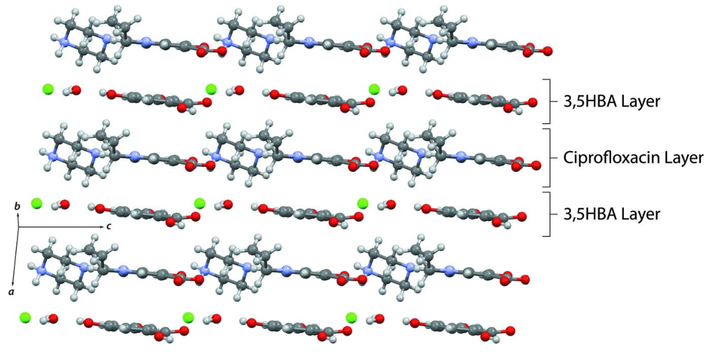
The crystal structure of two multi-component crystals of ciprofloxacin [systematic name: 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperazin-1-yl)quinoline-3-carboxylic acid], a fluoroquinolone antibiotic, namely, ciprofloxacin 2,6-dihydroxybenzoate salt, C17H19FN3O3+·C7H5O4−, (I), and ciprofloxacin hydrochloride–3,5-dihydroxybenzoic–water (1/1/1), C17H19FN3O3+·Cl−·C7H6O4·H2O, (II), were determined. In (I) and (II), the ciprofloxacin cations are connected via head-to-tail N—H⋯O hydrogen bonding. Both structures show an alternating layered arrangement between ciprofloxacin and dihydroxybenzoic acid.
Type
Publication
Acta Crystallographica Section E Crystallographic Communications